Swagger Support
[metosin/reitit-swagger "0.7.0-alpha7"]
Reitit supports Swagger2 documentation, thanks to schema-tools and spec-tools. Documentation is extracted from route definitions, coercion :parameters and :responses and from a set of new documentation keys.
See also: OpenAPI support.
To enable swagger-documentation for a Ring router:
- annotate your routes with swagger-data
- mount a swagger-handler to serve the swagger-spec
- optionally mount a swagger-ui to visualize the swagger-spec
Swagger data
The following route data keys contribute to the generated swagger specification:
| key | description |
|---|---|
| :swagger | map of any swagger-data. Can have :id (keyword or sequence of keywords) to identify the api |
| :no-doc | optional boolean to exclude endpoint from api docs |
| :tags | optional set of string or keyword tags for an endpoint api docs |
| :summary | optional short string summary of an endpoint |
| :description | optional long description of an endpoint. Supports http://spec.commonmark.org/ |
| :operationId | optional string specifying the unique ID of an Operation |
Coercion keys also contribute to the docs:
| key | description |
|---|---|
| :parameters | optional input parameters for a route, in a format defined by the coercion |
| :responses | optional descriptions of responses, in a format defined by coercion |
There is a reitit.swagger.swagger-feature, which acts as both a Middleware and an Interceptor that is not participating in any request processing - it just defines the route data specs for the routes it's mounted to. It is only needed if the route data validation is turned on.
Swagger spec
To serve the actual Swagger Specification, there is reitit.swagger/create-swagger-handler. It takes no arguments and returns a ring-handler which collects at request-time data from all routes for the same swagger api and returns a formatted Swagger specification as Clojure data, to be encoded by a response formatter.
If you need to post-process the generated spec, just wrap the handler with a custom Middleware or an Interceptor.
Swagger-ui
Swagger-ui is a user interface to visualize and interact with the Swagger specification. To make things easy, there is a pre-integrated version of the swagger-ui as a separate module.
[metosin/reitit-swagger-ui "0.7.0-alpha7"]
reitit.swagger-ui/create-swagger-ui-handler can be used to create a ring-handler to serve the swagger-ui. It accepts the following options:
| key | description |
|---|---|
| :parameter | optional name of the wildcard parameter, defaults to unnamed keyword : |
| :root | optional resource root, defaults to "swagger-ui" |
| :url | path to swagger endpoint, defaults to /swagger.json |
| :path | optional path to mount the handler to. Works only if mounted outside of a router. |
| :config | parameters passed to swagger-ui as-is. See the docs |
We use swagger-ui from ring-swagger-ui, which can be easily configured from routing application. It stores files swagger-ui in the resource classpath.
Webjars also hosts a version of the swagger-ui.
NOTE: Currently, swagger-ui module is just for Clojure. ClojureScript-support welcome as a PR!
NOTE: If you want to use swagger-ui 2.x you can do so by explicitly downgrading metosin/ring-swagger-ui to 2.2.10.
NOTE: If you use swagger-ui 3.x, you need to include :responses for Swagger-UI
to display the response when trying out endpoints. You can define :responses {200 {:schema s/Any}}
at the top-level to show responses for all endpoints.
Examples
Simple example
- two routes
- swagger-spec served from
"/swagger.json" - swagger-ui mounted to
"/api-docs" - note that for real-world use, you need a content-negotiation middleware - see the next example
(require '[reitit.ring :as ring])
(require '[reitit.swagger :as swagger])
(require '[reitit.swagger-ui :as swagger-ui])
(def app
(ring/ring-handler
(ring/router
[["/api"
["/ping" {:get (constantly {:status 200, :body "ping"})}]
["/pong" {:post (constantly {:status 200, :body "pong"})}]]
["" {:no-doc true}
["/swagger.json" {:get (swagger/create-swagger-handler)}]
["/api-docs/*" {:get (swagger-ui/create-swagger-ui-handler)}]]])))
The generated swagger spec:
(app {:request-method :get :uri "/swagger.json"})
;{:status 200
; :body {:swagger "2.0"
; :x-id #{:reitit.swagger/default}
; :paths {"/api/ping" {:get {}}
; "/api/pong" {:post {}}}}}
Swagger-ui:
(app {:request-method :get, :uri "/api-docs/index.html"})
; ... the swagger-ui index-page, configured correctly
You might be interested in adding a trailing slash handler to the app to serve the swagger-ui from /api-docs (without the trailing slash) too.
Another way to serve the swagger-ui is using the default handler:
(def app
(ring/ring-handler
(ring/router
[["/api"
["/ping" {:get (constantly {:status 200, :body "ping"})}]
["/pong" {:post (constantly {:status 200, :body "pong"})}]]
["/swagger.json"
{:get {:no-doc true
:handler (swagger/create-swagger-handler)}}]])
(swagger-ui/create-swagger-ui-handler {:path "/api-docs"})))
More complete example
clojure.speccoercion- swagger data (
:tags,:produces,:summary,:basePath) - swagger-spec served from
"/swagger.json" - swagger-ui mounted to
"/" - set of middleware for content negotiation, exceptions, multipart etc.
- missed routes are handled by
create-default-handler - served via ring-jetty
Whole example project is in /examples/ring-spec-swagger.
(ns example.server
(:require [reitit.ring :as ring]
[reitit.swagger :as swagger]
[reitit.swagger-ui :as swagger-ui]
[reitit.ring.coercion :as coercion]
[reitit.coercion.spec]
[reitit.ring.middleware.muuntaja :as muuntaja]
[reitit.ring.middleware.exception :as exception]
[reitit.ring.middleware.multipart :as multipart]
[reitit.ring.middleware.parameters :as parameters]
[ring.middleware.params :as params]
[ring.adapter.jetty :as jetty]
[muuntaja.core :as m]
[clojure.java.io :as io]))
(def app
(ring/ring-handler
(ring/router
[["/swagger.json"
{:get {:no-doc true
:swagger {:info {:title "my-api"}
:basePath "/"} ;; prefix for all paths
:handler (swagger/create-swagger-handler)}}]
["/files"
{:swagger {:tags ["files"]}}
["/upload"
{:post {:summary "upload a file"
:parameters {:multipart {:file multipart/temp-file-part}}
:responses {200 {:body {:file multipart/temp-file-part}}}
:handler (fn [{{{:keys [file]} :multipart} :parameters}]
{:status 200
:body {:file file}})}}]
["/download"
{:get {:summary "downloads a file"
:swagger {:produces ["image/png"]}
:handler (fn [_]
{:status 200
:headers {"Content-Type" "image/png"}
:body (io/input-stream (io/resource "reitit.png"))})}}]]
["/math"
{:swagger {:tags ["math"]}}
["/plus"
{:get {:summary "plus with spec query parameters"
:parameters {:query {:x int?, :y int?}}
:responses {200 {:body {:total int?}}}
:handler (fn [{{{:keys [x y]} :query} :parameters}]
{:status 200
:body {:total (+ x y)}})}
:post {:summary "plus with spec body parameters"
:parameters {:body {:x int?, :y int?}}
:responses {200 {:body {:total int?}}}
:handler (fn [{{{:keys [x y]} :body} :parameters}]
{:status 200
:body {:total (+ x y)}})}}]]]
{:data {:coercion reitit.coercion.spec/coercion
:muuntaja m/instance
:middleware [;; query-params & form-params
parameters/parameters-middleware
;; content-negotiation
muuntaja/format-negotiate-middleware
;; encoding response body
muuntaja/format-response-middleware
;; exception handling
exception/exception-middleware
;; decoding request body
muuntaja/format-request-middleware
;; coercing response bodys
coercion/coerce-response-middleware
;; coercing request parameters
coercion/coerce-request-middleware
;; multipart
multipart/multipart-middleware]}})
(ring/routes
(swagger-ui/create-swagger-ui-handler {:path "/"})
(ring/create-default-handler))))
(defn start []
(jetty/run-jetty #'app {:port 3000, :join? false})
(println "server running in port 3000"))
http://localhost:3000 should render now the swagger-ui:
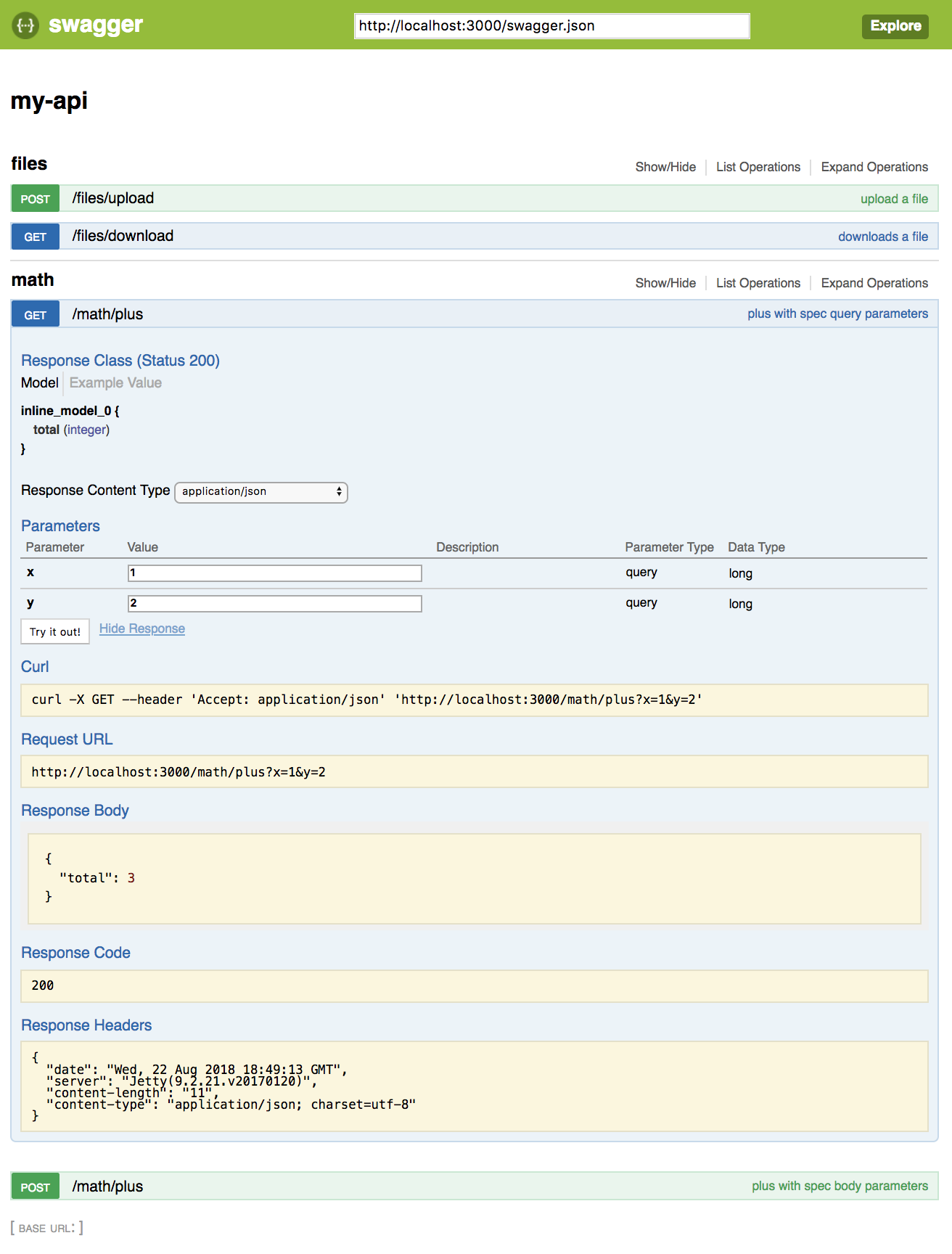
Multiple swagger apis
There can be multiple swagger apis within a router. Each route can be part of 0..n swagger apis. Swagger apis are identified by value in route data under key path [:swagger :id]. It can be either a keyword or a sequence of keywords. Normal route data scoping rules rules apply.
Example with:
- 4 routes
- 2 swagger apis
::oneand::two - 3 swagger specs
(require '[reitit.ring :as ring])
(require '[reitit.swagger :as swagger])
(def ping-route
["/ping" {:get (constantly {:status 200, :body "ping"})}])
(def spec-route
["/swagger.json"
{:get {:no-doc true
:handler (swagger/create-swagger-handler)}}])
(def app
(ring/ring-handler
(ring/router
[["/common" {:swagger {:id #{::one ::two}}} ping-route]
["/one" {:swagger {:id ::one}} ping-route spec-route]
["/two" {:swagger {:id ::two}} ping-route spec-route
["/deep" {:swagger {:id ::one}} ping-route]]
["/one-two" {:swagger {:id #{::one ::two}}} spec-route]])))
(-> {:request-method :get, :uri "/one/swagger.json"} app :body :paths keys)
; ("/common/ping" "/one/ping" "/two/deep/ping")
(-> {:request-method :get, :uri "/two/swagger.json"} app :body :paths keys)
; ("/common/ping" "/two/ping")
(-> {:request-method :get, :uri "/one-two/swagger.json"} app :body :paths keys)
; ("/common/ping" "/one/ping" "/two/ping" "/two/deep/ping")
TODO
- ClojureScript
- example for Macchiato
- body formatting
- resource handling